一.初识Redis
1.什么是Redis与Redis配置
Redis是一种键值型的NoSql数据库。有两个关键词:
键值型
NoSql
特点:**C语言开发 基于内存 开源 键值对(key-value)结构数据库
高性能,官方提供的数据是可以达到100000+的QPS(每秒内查询次数),简单说就是查询快。
但因为是基于内存的,内存又有限,所以一般用来存热点数据(短时间或者经常访问)。
【1】键值型
指Redis中存储的数据都是以key,value堆的形式存储,而value的形式多种多样,可以是字符串,数值,甚至是json:

【2】NoSql
NoSql可以翻译做Not Only Sql(不仅仅是SQL),或者是No Sql(非Sql的)数据库。称被之为非关系型数据库。NoSql数据库并不是要取代非关系型数据库,而是关系型数据库的补充。
(1)结构化与非结构化
传统关系型数据库是结构化数据,每一张表都有严格的约束信息:字段名,字段数据类型,字段约束等等信息,插入的数据必须遵循这些约束:

而NoSql数据库格式没有严格要求,可以是键值型,文档型,甚至可以是图格型。
(2)关联与非关联
传统数据库表与表之间往往存在关联,例如外键。而非关系型数据库不存在关联关系,要维护关系只能靠代码业务逻辑和数据之间的耦合。
(3)查询
非关系型数据库语法差异大。
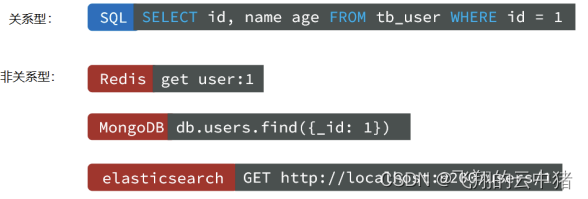
(4)事务
非关系型数据库往往不支持事务,或者不能严格保证ACID的特性。
应用场景:缓存,任务队列,消息队列,分布式锁等。
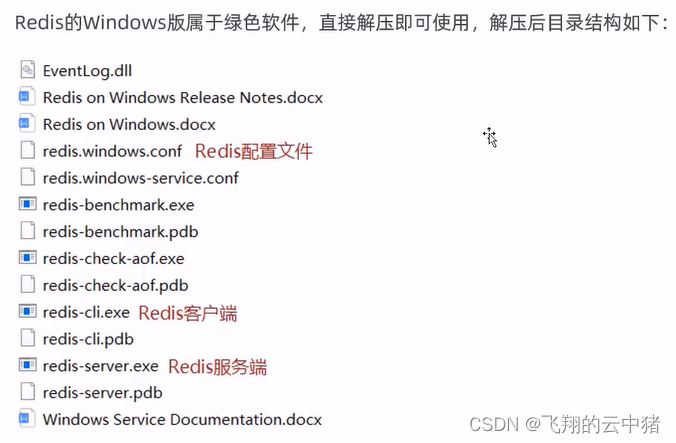
2.Redis下载与安装


3.Redis服务启动与停止
【1】启动服务
Linux中使用redis-server命令启动redis服务,默认端口号为6379。(在所有位置都能使用redis-server)
ctrl+c停止Redis服务;或者ps -ef | grep ‘redis’查看对应的进程 kill -9 进程号来停止Redis服务。
将redis-server挂后台运行,或者再开一个控制台
然后cd /usr/local/redis-4.0.0/src(定位到redis文件夹,找不到的可以用find命令)
然后输入redis-cli就可以启动客户端
在Windows上点击redis-server.exe,就可以启动服务端,然后再点击redis-cli.exe就可以启用客户端输入命令。
【2】远程连接
修改配置文件让redis在后台运行
修改配置文件让客户端需要密码认证
修改配置文件让服务端可以被远程客户端连接
修改完配置文件后怎么重启redis
怎么用控制台让Windows的redis-cli远程连接linux的redis-server
二.Redis数据类型
Redis存储的是key-value数据类型,其中Key是字符串类型,value是5种常用的数据类型:
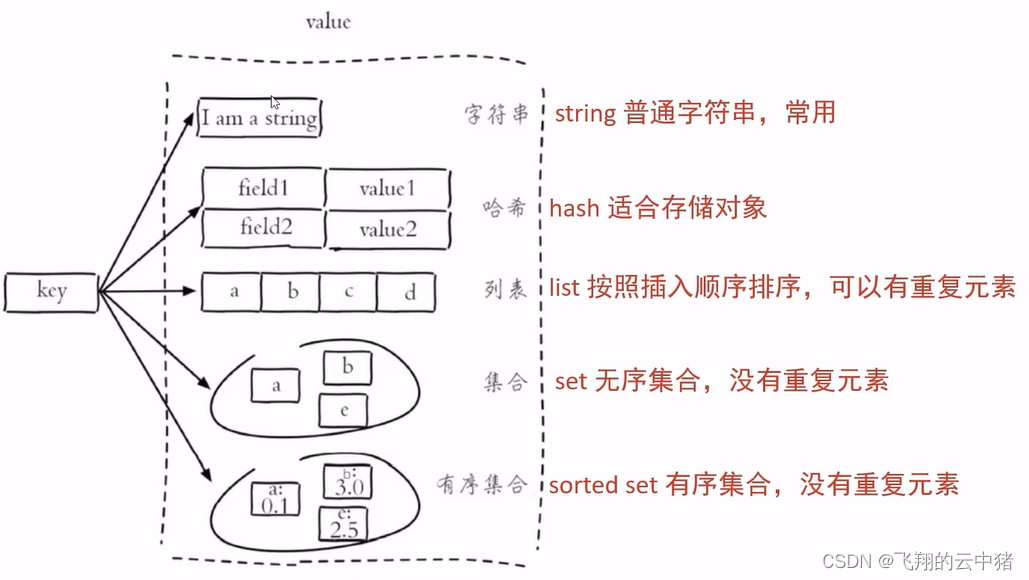



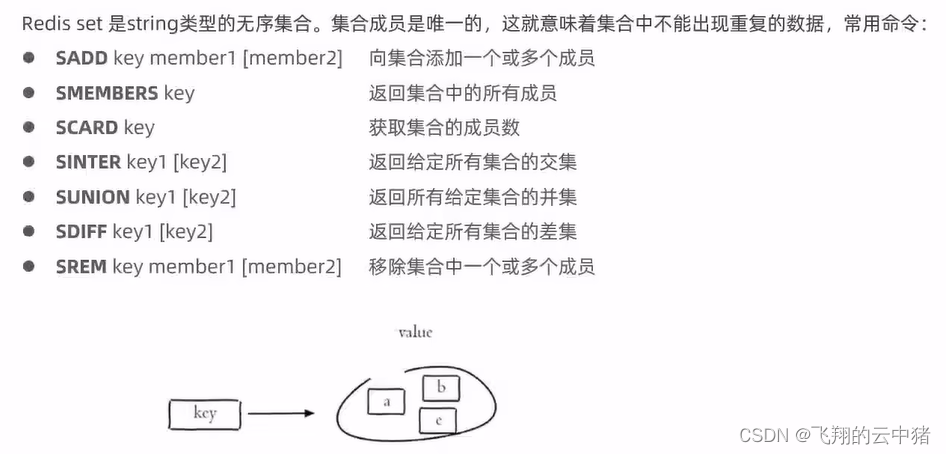

更多命令可以到这个网站学习:redis命令手册
三.在Java中操作Reidis
1.介绍
Redis的Java客户端很多,官方推荐的有三种:Jedis,Lettuce,Redisson
Spring对Redis客户端进行了整合,提供了Spring Data Redis,在Spring Boot项目中还提供了对应的Start,即spring-boot-start-data-redis。
2.Jedis(只是简单介绍一下)
导入依赖与一个小demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
| <dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
import org.junit.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.Set;
public class jedisTest {
@Test
public void testRedis(){
Jedis jedis=new Jedis("localhost",6379);
jedis.set("username","xiaoming");
String value=jedis.get("username");
System.out.println(value);
jedis.hset("myhash","addr","bj");
String hValue = jedis.hget( "myhash", "addr");
System.out.println(hValue);
Set<String> keys=jedis.keys("*");
for(String key:keys){
System.out.println(key);
}
jedis.close();
}
}
|
3.Spring Data Redis入门(底层是对jedis做的封装)
【1】导入依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
|

【2】Spring Data Redis的使用非常简单,只需要用@Autowired注入RedisTemplate(因为下面是测试类,所以需要用@Resource注入)就可以调用RedisTemplate里面的方法操作redis了。
例如下面在redis中添加了键值对city:beijing
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| @SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class SpringDataRedisTest {
@Resource
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void testString(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("city","beijing");
}
}
|
【3】配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
#spring.redis.password=123456
#redis为我们提供16个数据库(具体数量可以在配置文件下载),默认操作0号数据库
spring.redis.database=0
#Redis连接池配置
##最大连接数
#spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active
##连接池最小空塞等待时间
#spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait
##连接池中的最大空闲时间
#spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle
##连接池中的最小空闲时间
#spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle
|
【4】执行上面的代码后打开redis客户端执行key *命令,我们会发现key不是city,只是因为序列化的缘故,所以我们还需要添加配置类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
| @Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
@SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory)
{
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
FastJsonRedisSerializer serializer = new FastJsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
|
【5】我们还会将RedisTemplate的方法进一步封装为工具类
这是我在网上找的一个工具类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
679
680
681
682
683
684
685
686
687
688
689
690
691
692
693
694
695
696
697
698
699
700
701
702
703
704
705
706
707
708
709
710
711
712
713
714
715
716
717
718
719
720
721
722
723
724
725
726
727
728
729
730
731
732
733
734
735
736
737
738
739
740
741
742
743
744
745
746
747
748
749
750
751
752
753
754
755
756
757
758
759
760
761
762
763
764
765
766
767
768
769
770
771
772
773
774
775
776
777
778
779
780
781
782
783
784
785
786
787
788
789
790
791
792
793
794
795
796
797
798
799
800
801
802
803
804
805
806
807
808
809
810
811
812
813
814
815
816
817
818
819
820
821
822
823
824
825
826
827
828
829
830
831
832
833
834
835
836
837
838
839
840
841
842
843
844
845
846
847
848
849
850
851
852
853
854
855
856
857
858
859
860
861
862
863
864
865
866
867
868
869
870
871
872
873
874
875
876
877
878
879
880
881
882
883
884
885
886
887
888
889
890
891
892
893
894
895
896
897
898
899
900
901
902
903
904
905
906
907
908
909
910
911
912
913
914
915
916
917
918
919
920
921
922
923
924
925
926
927
928
929
930
931
932
933
934
935
936
937
938
939
940
941
942
943
944
945
946
947
948
949
| package com.flyingpig.util;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.BoundSetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SuppressWarnings(value = { "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
@Component
public class RedisCache
{
@Autowired
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
/**
* 缓存基本的对象,Integer、String、实体类等
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param value 缓存的值
* @param timeout 时间
* @param timeUnit 时间颗粒度
*/
public <T> void setCacheObject(final String key, final T value, final Integer timeout, final TimeUnit timeUnit)
{
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, timeout, timeUnit);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout)
{
return expire(key, timeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 设置有效时间
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param unit 时间单位
* @return true=设置成功;false=设置失败
*/
public boolean expire(final String key, final long timeout, final TimeUnit unit)
{
return redisTemplate.expire(key, timeout, unit);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象。
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> T getCacheObject(final String key)
{
ValueOperations<String, T> operation = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
return operation.get(key);
}
/**
* 删除单个对象
*
* @param key
*/
public boolean deleteObject(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
/**
* 删除集合对象
*
* @param collection 多个对象
* @return
*/
public long deleteObject(final Collection collection)
{
return redisTemplate.delete(collection);
}
/**
* 缓存List数据
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @param dataList 待缓存的List数据
* @return 缓存的对象
*/
public <T> long setCacheList(final String key, final List<T> dataList)
{
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, dataList);
return count == null ? 0 : count;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的list对象
*
* @param key 缓存的键值
* @return 缓存键值对应的数据
*/
public <T> List<T> getCacheList(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0, -1);
}
/**
* 缓存Set
*
* @param key 缓存键值
* @param dataSet 缓存的数据
* @return 缓存数据的对象
*/
public <T> BoundSetOperations<String, T> setCacheSet(final String key, final Set<T> dataSet)
{
BoundSetOperations<String, T> setOperation = redisTemplate.boundSetOps(key);
Iterator<T> it = dataSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
setOperation.add(it.next());
}
return setOperation;
}
/**
* 获得缓存的set
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Set<T> getCacheSet(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
}
/**
* 缓存Map
*
* @param key
* @param dataMap
*/
public <T> void setCacheMap(final String key, final Map<String, T> dataMap)
{
if (dataMap != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, dataMap);
}
}
/**
* 获得缓存的Map
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public <T> Map<String, T> getCacheMap(final String key)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
}
/**
* 往Hash中存入数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @param value 值
*/
public <T> void setCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey, final T value)
{
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, hKey, value);
}
/**
* 获取Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKey Hash键
* @return Hash中的对象
*/
public <T> T getCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hKey)
{
HashOperations<String, String, T> opsForHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return opsForHash.get(key, hKey);
}
/**
* 删除Hash中的数据
*
* @param key
* @param hkey
*/
public void delCacheMapValue(final String key, final String hkey)
{
HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hashOperations.delete(key, hkey);
}
/**
* 获取多个Hash中的数据
*
* @param key Redis键
* @param hKeys Hash键集合
* @return Hash对象集合
*/
public <T> List<T> getMultiCacheMapValue(final String key, final Collection<Object> hKeys)
{
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, hKeys);
}
/**
* 获得缓存的基本对象列表
*
* @param pattern 字符串前缀
* @return 对象列表
*/
public Collection<String> keys(final String pattern)
{
return redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
}
}
|
但我感觉他的好多方法都是一句话,封装了和没封装好像差不多。
然后的话我们在别的类中
1
2
3
4
5
| @Autowired
private RedisCache redisCache;
|
就可以使用这个工具类了。例如我们可以在登录的使用将用户信息存入redis中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
LoginUser loginUser = (LoginUser) authenticate.getPrincipal();
String userid = loginUser.getUser().getId().toString();
String jwt = JwtUtil.createJWT(userid);
redisCache.setCacheObject("login:"+userid,loginUser);
|
4.Spring Cache框架
Spring Cache 是一个框架,实现了基于注解的缓存功能,只需要简单地加一个注解,就能实现缓存功能。
Spring Cache 提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的缓存实现,例如:
【1】EHCache
【2】Caffeine
【3】Redis(常用)
起步依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
常用注解
在SpringCache中提供了很多缓存操作的注解,常见的是以下的几个:
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @EnableCaching |
开启缓存注解功能,通常加在启动类上 |
| @Cacheable |
在方法执行前先查询缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;如果没有缓存数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CachePut |
将方法的返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CacheEvict |
将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |












